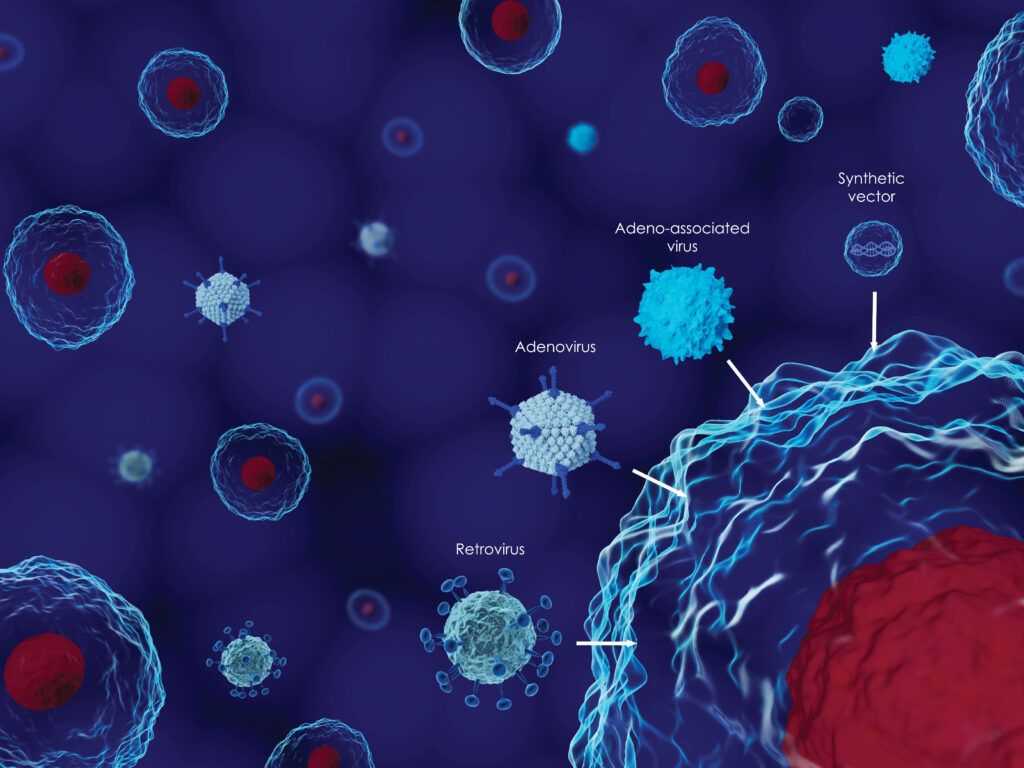
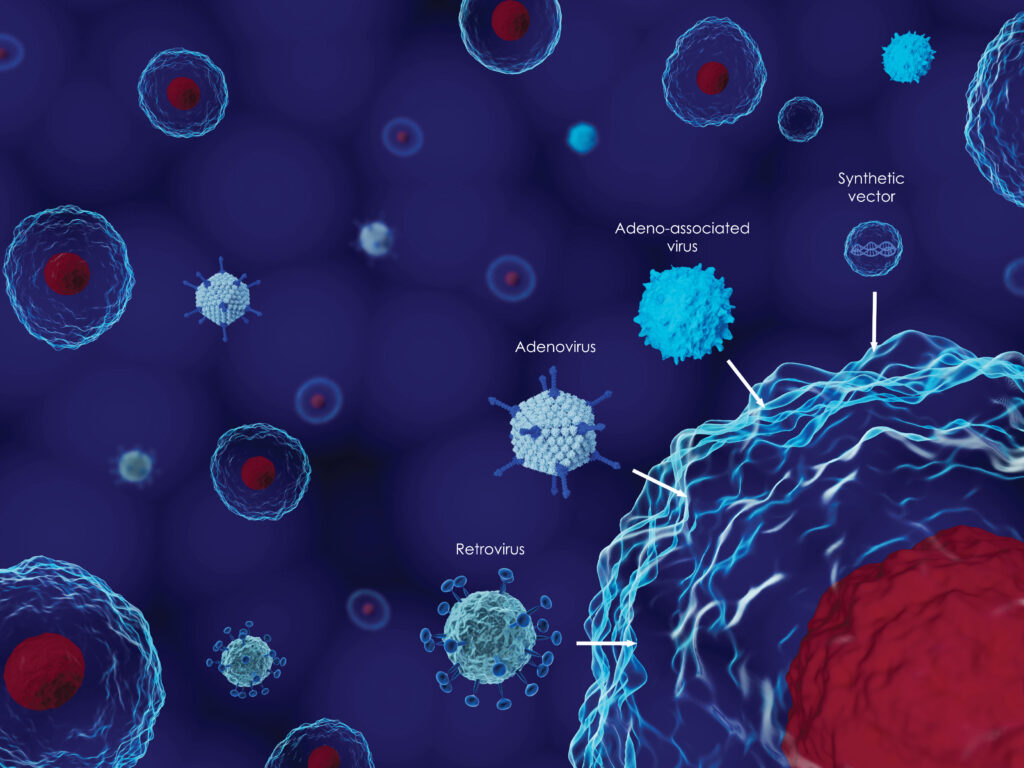
Viruses are one of the most numerous groups in the biological world. About 80% of clinical infectious diseases are caused by viruses. Up to now, more than 400 viruses have been found to have pathogenic effects on humans, involving 27 virus families, which are collectively referred to as human viruses.
The relationship between viral infection and clinical disease is very close, and the clinical manifestations of the disease are varied. Some viral infections may have specific clinical symptoms and signs, which are called dominant infections; some viral infections may have no obvious symptoms or show a subclinical infection state, which is called latent infections; some viral infections are acute and self-limiting clinical course. After the disease, the body can obtain persistent immunity, such as hepatitis A; some viral infections can be in a latent or static state. Once the body is stimulated by certain factors or the immunity is weakened, it can be transformed into an active state and cause the disease, such as chickenpox. - Herpes zoster virus infection. Some viruses cause only acute infection, while others can not only cause acute infection, but can also become persistent infection with serious consequences, such as retroviral infection. Retroviruses can also cause latent infection, which integrates viral genes into the chromosomes of host cells and does not replicate. Under specific conditions, viral genes are activated, virus replicated and released, resulting in tissue damage and clinical symptoms, which can even lead to Diseases that threaten human life.
The infection mechanism of viruses to humans is complex. Different viruses can cause lesions in the same organ or tissue. For example, known viruses that can cause diarrhea include rotavirus, adenovirus, coronavirus, and other enteroviruses. Viruses that can cause acute respiratory diseases include adenovirus, influenza virus, parainfluenza virus, mumps virus, respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus. Viruses that can cause central nervous system lesions include Japanese encephalitis virus, polio virus, coxsackie virus, measles virus and rabies virus. On the other hand, the same virus can cause lesions in multiple organs or tissues, such as herpes simplex virus can cause pharyngitis, genital inflammation, conjunctivitis and encephalitis. Tumor is a disease that seriously threatens human health and life safety, and is one of the three major causes of human death. Many human tumors are associated with viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus (Epstein-Barr virus) and nasopharyngeal cancer, human papillomavirus (papillomavirus) and cervical cancer, human herpesvirus 8 and Kaposi's sarcoma, hepatitis B virus and Hepatocellular carcinoma, etc. In recent years, organ transplantation has developed rapidly. However, due to the use of a large number of immunosuppressive agents after organ transplantation, CMV, V-ZV and HBV infection have become important reasons for transplantation failure or hepatitis recurrence.
Improving the clinical understanding of viral diseases, exploring the causal relationship and pathogenesis of various diseases and viral infections, and continuously improving the diagnosis and treatment techniques of viral diseases are the research directions and important topics for clinical prevention and treatment of viral diseases.
If the virus is classified according to the clinical characteristics of viral infection, the virus can be divided into enterovirus, respiratory virus, arbovirus, hemorrhagic fever virus, hepatitis virus, retrovirus, adenovirus, human herpes virus, human papilloma virus , other viruses and subviruses, etc.