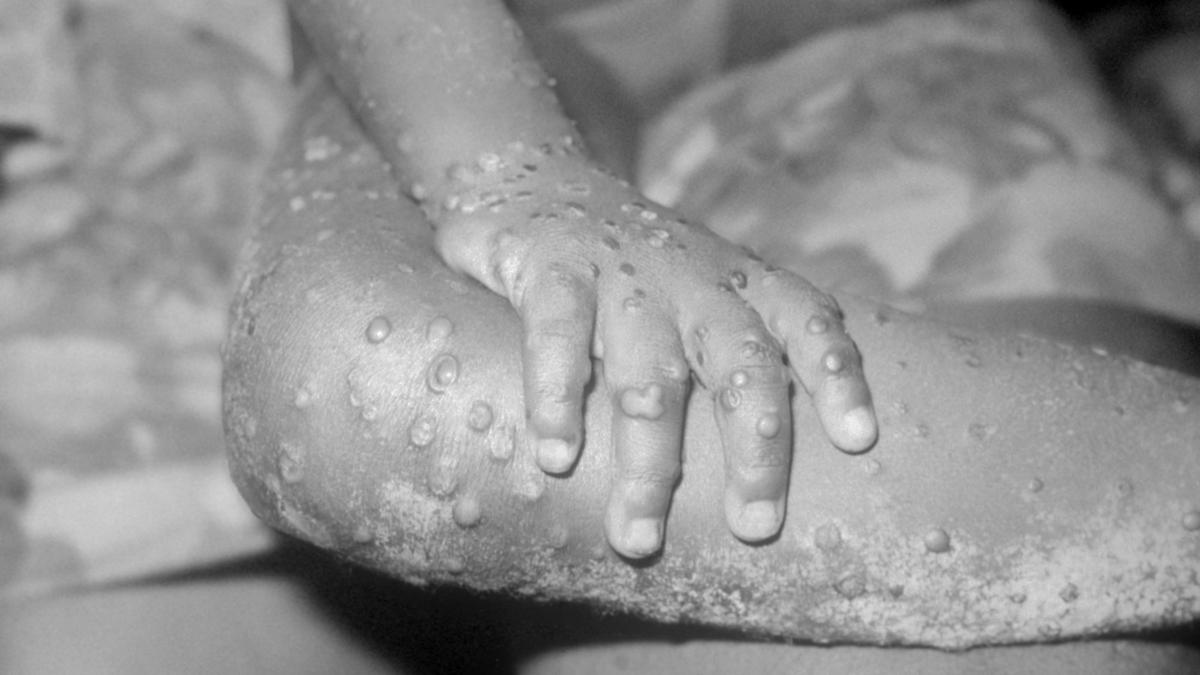
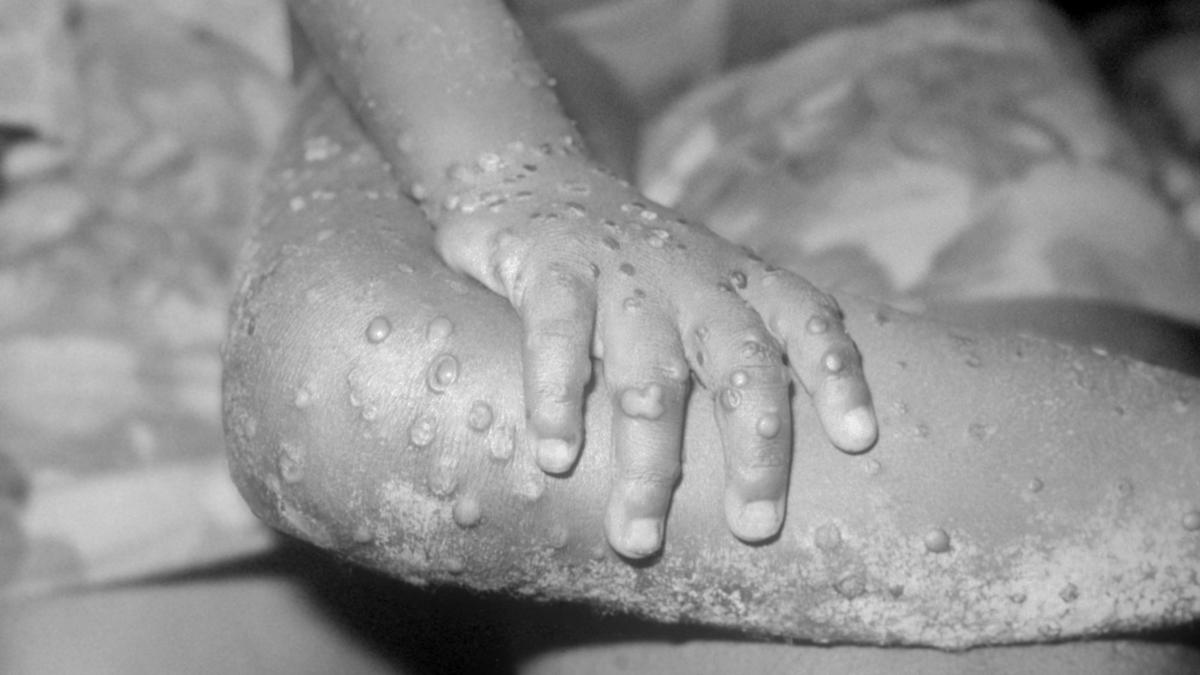
Monkeypox is a zoonotic disease. The main hosts are rodents such as squirrels and rabbits. Humans are infected with monkeypox mainly through bites by infected animals, or direct contact with the blood and body fluids of infected animals. Human-to-human transmission is rare. Human-to-human transmission includes close contact with patients' respiratory secretions, skin lesions or infected Contaminated items, etc., usually take longer face-to-face for respiratory droplet transmission to occur. In addition, monkeypox virus can also be transmitted through mother-to-child and sexual transmission. The incubation period for monkeypox is usually 5-21 days. In the early stages of the disease, patients present with fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, and swollen lymph nodes. Usually within 1-3 days after the fever, the patient will develop a rash of varying degrees, which spreads from the face to other parts of the body. At this time, the patient is contagious. Most patients recover within a few weeks of onset, but others become severely ill and even die. WHO data shows that the smallpox vaccine is 85% effective against monkeypox virus.
For ourselves, we should avoid contact with animals that may carry monkeypox virus (such as wild or unknown monkeys, rodents, etc.), and do not travel to countries and regions with monkeypox outbreaks. At this stage, wearing masks, maintaining hand hygiene, opening windows for ventilation, and daily disinfection are still very effective preventive measures.